8 Essential Data Migration Best Practices for 2025
Data migration is more than just moving files from one place to another; it's a critical business operation that carries significant risk. A flawed migration can lead to catastrophic data loss, extended operational downtime, and severe damage to an organisation's reputation. For professional services firms, care providers, and accountants across Dorset, Somerset, Wiltshire, and Hampshire, where data integrity and availability are paramount, the stakes are exceptionally high. A single misstep during a cloud migration or system upgrade can compromise sensitive client information, disrupt essential services, and lead to serious compliance breaches.
The complexity of modern IT environments, from on-premises servers to intricate cloud architectures, means that a 'lift and shift' approach is no longer viable. Success hinges on a meticulously planned and expertly executed strategy. This is where adhering to proven data migration best practices becomes essential. It is the difference between a seamless transition that enhances business capabilities and a costly failure that requires extensive remediation efforts. This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive, actionable framework for your next migration project.
We will detail eight fundamental best practices, offering practical implementation steps and real-world examples relevant to your sector. Following this structured methodology will empower you to navigate the complexities of data transfer, whether you are upgrading internal systems, moving to a new cloud provider, or consolidating data centres. By implementing these professional guidelines, you will be equipped to protect your data's integrity, minimise disruption, and ensure your project delivers on its strategic promises without compromising on security or performance.
1. Comprehensive Data Assessment and Planning
A successful data migration is built on a foundation of deep understanding. Comprehensive data assessment and planning is the crucial first step where you meticulously analyse the source data’s quality, structure, complexity, and volume before any migration activity begins. This foundational practice involves cataloguing every data asset, from databases to unstructured files, to create a complete picture of your data landscape.
This initial discovery phase is non-negotiable for mitigating risks. It allows your team to identify potential roadblocks, such as corrupt data, duplicate records, or complex interdependencies between systems, long before they can derail the project. By understanding exactly what you are moving, you can create a realistic, detailed, and resource-aware migration plan.

Why This Practice is Essential
Without a thorough assessment, organisations often discover critical issues mid-migration, leading to costly delays, data loss, and significant business disruption. This is one of the most vital data migration best practices because it transforms the process from a high-risk gamble into a predictable and controlled project. It ensures that the target system is fit for purpose and that the data populating it will be accurate, consistent, and valuable from day one.
For a professional services firm, this might involve a deep analysis of their client relationship management (CRM) system. Before migrating to a new platform like Salesforce, they would need to assess decades of client contact data, project histories, and billing information. This allows them to identify obsolete records for archival and map critical fields correctly, ensuring a smooth transition without losing valuable client intelligence.
"Skipping a detailed data assessment is like setting out on a cross-country journey without a map, a fuel gauge, or an understanding of the terrain. You are planning for failure."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Utilise Automated Tools: Employ automated data profiling and discovery tools to accelerate the assessment process. These tools can quickly scan source systems to identify data types, formats, quality issues, and relationships, saving hundreds of manual hours.
- Involve Business Stakeholders: Data is a business asset. Involve department heads and key users (e.g., from accounting or client management) in the validation process. They possess the contextual knowledge to confirm what data is critical, what is obsolete, and what defines "quality" for their operations.
- Establish Data Quality Metrics: Before you begin, define what "good" data looks like. Establish clear metrics and thresholds for completeness, accuracy, and consistency. For instance, a care provider might mandate that 99.8% of patient records must have a valid NHS number.
- Create Data Lineage Diagrams: For complex systems, map out the data's journey. Data lineage diagrams visually represent how data flows between different applications and databases, making it easier to identify dependencies that could break during migration.
- Document Everything: Maintain a centralised repository for all findings, including data dictionaries, quality reports, and stakeholder decisions. This document becomes the single source of truth for the entire migration team.
2. Robust Data Backup and Recovery Strategy
No data migration is entirely without risk. A robust data backup and recovery strategy is your non-negotiable insurance policy, providing a safety net to protect your operations against unforeseen complications, data corruption, or catastrophic failure during the transition. This practice involves creating complete, validated copies of your source data before migration begins and establishing clear, tested procedures to restore it if necessary.
This strategy is about more than just clicking "backup"; it’s a comprehensive plan that defines when backups are taken, where they are stored, and precisely how they will be restored. A well-designed approach ensures that if the migration encounters a critical error, the business can quickly revert to the last known stable state, minimising costly downtime and preventing irreversible data loss.

Why This Practice is Essential
Without a tested recovery plan, a migration failure can become a business-ending event. This is one of the most critical data migration best practices because it directly addresses the highest-stakes risks: data loss and extended operational disruption. It gives your organisation the confidence to proceed with a complex technical project, knowing that a viable rollback path exists at all times.
Consider an accountancy firm migrating its main practice management software over a weekend. A robust backup strategy would involve taking a full, application-aware snapshot of the server just before the migration begins. If, on Sunday evening, testing reveals critical errors in client ledgers on the new system, the team can use the snapshot to restore the original system to its exact pre-migration state, ensuring the firm is fully operational for business on Monday morning. You can learn more about backing up data on sescomputers.com.
"A backup that has not been tested is not a backup; it is merely a hope. A recovery strategy lives or dies on its proven ability to restore operations."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Implement the 3-2-1 Backup Rule: Maintain at least three copies of your data, store them on two different types of media, and keep one copy off-site or in a separate cloud environment. This is the gold standard for data resilience.
- Test Backup Restoration: Before the migration starts, perform a full test restore of your backup to a separate, isolated environment. This validates the integrity of the backup files and confirms your recovery procedure works as expected.
- Use Immutable Storage: Store a copy of your pre-migration backup in immutable storage. This technology prevents the data from being altered or deleted, even by system administrators, providing a critical defence against ransomware or accidental changes.
- Document the Recovery Process: Create a clear, step-by-step recovery guide. This document should be accessible to key personnel and detail every action required to restore the system, from technical commands to stakeholder communication protocols.
- Schedule Backup Integrity Checks: Regularly run automated checks on your backup files to ensure they are not corrupt and are fully readable. This prevents the nightmare scenario of discovering your safety net is unusable at the moment of crisis.
3. Phased Migration Approach
A phased migration approach strategically breaks down a large-scale data transfer into a series of smaller, more manageable stages or waves. Instead of a high-risk, "big bang" switchover, this method allows organisations to migrate data incrementally, system by system, or department by department. This iterative process provides control and reduces the complexity of an otherwise overwhelming task.
By tackling the migration in distinct phases, teams can test, validate, and learn from each stage before proceeding to the next. This controlled rollout minimises business disruption, as only a small part of the operation is affected at any given time. It transforms a monumental project into a predictable sequence of well-defined steps, making it an essential strategy for complex, mission-critical systems.
The following process flow illustrates the sequential nature of a phased migration, moving from low-risk pilots to core system transfers and final validation.
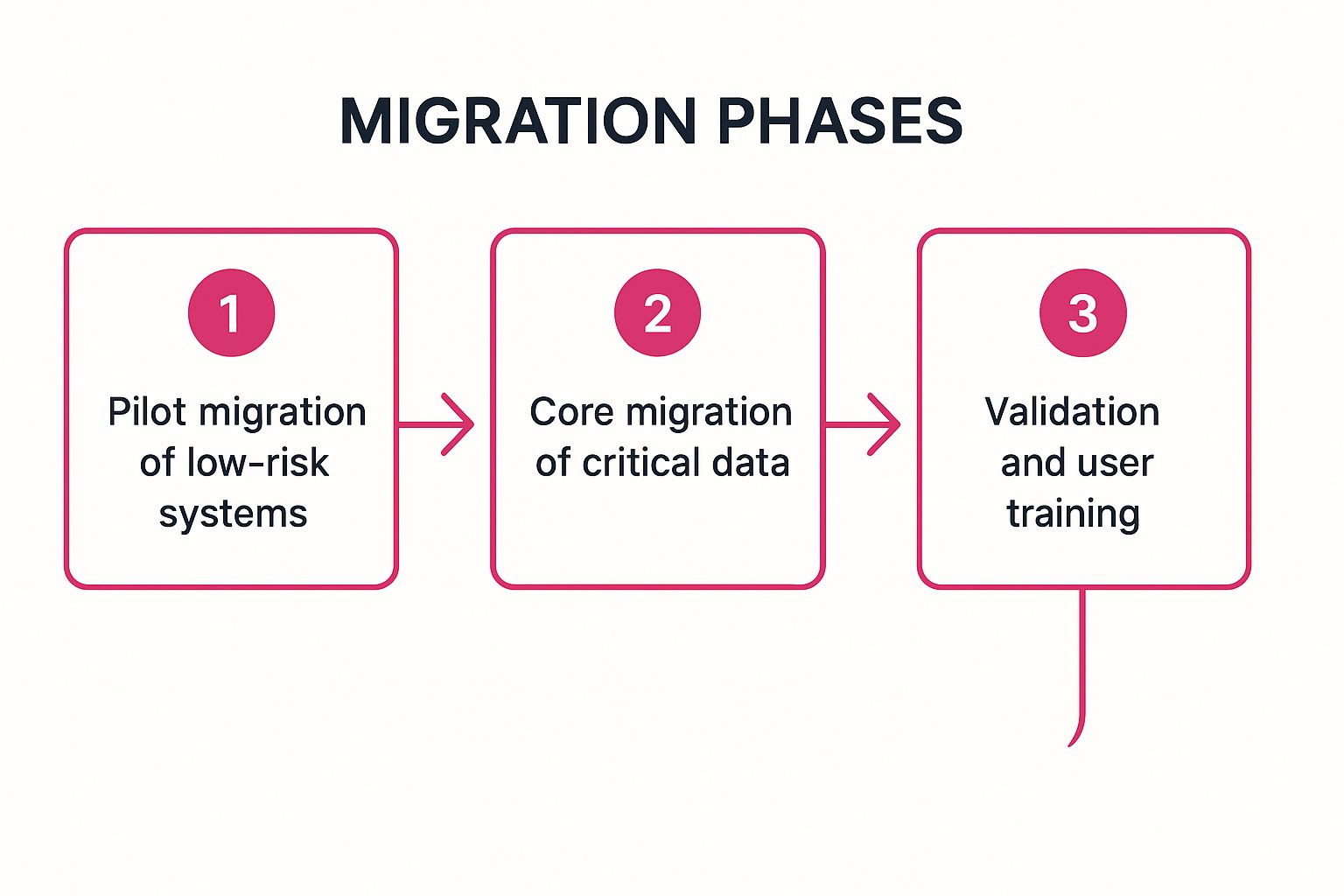
This visualisation highlights how each phase builds upon the success of the last, ensuring a structured and controlled progression throughout the project.
Why This Practice is Essential
Attempting to migrate an entire enterprise's data in one go is fraught with peril. A single unforeseen issue can cause catastrophic failure, leading to extended downtime, data corruption, and significant financial loss. This makes the phased approach one of the most vital data migration best practices for risk management. It contains the potential impact of any problems to a single, isolated phase, which can be addressed without jeopardising the entire project.
For example, a regional law firm migrating its document management system could first move its archived cases (low-risk data). The next phase could involve the corporate law department, followed by the litigation team. This allows the IT team to resolve any unforeseen issues with a smaller user group before impacting the entire firm, ensuring minimal disruption to active client matters.
"A phased migration isn't about moving slowly; it's about moving smartly. It trades the illusion of speed for the certainty of success, one validated step at a time."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Prioritise Low-Risk Phases: Begin with less critical data or systems. Migrating a departmental archive or a secondary application first serves as a valuable proof of concept, allowing your team to refine processes and resolve issues with minimal business impact.
- Establish Clear Completion Criteria: For each phase, define specific, measurable criteria for success. This could include data validation pass rates, system performance benchmarks, and user acceptance testing sign-offs. A phase is only complete when these targets are met.
- Plan for Data Synchronisation: During the migration, both old and new systems may need to operate concurrently. Implement a robust strategy for keeping data synchronised between the source and target systems to ensure operational continuity and data integrity.
- Create Rollback Plans for Each Phase: Despite careful planning, issues can arise. Develop and test a specific rollback plan for every individual phase. This ensures you can quickly revert to the previous stable state if a critical problem is discovered post-migration.
- Schedule Regular Phase Reviews: After completing each wave, hold a review meeting with all key stakeholders, including technical teams and business users. Use this opportunity to discuss lessons learned, analyse what worked, and adjust the plan for subsequent phases.
4. Comprehensive Testing and Validation Framework
A robust testing and validation framework is the quality assurance backbone of any data migration project. It is a systematic process for verifying the accuracy, completeness, and functionality of data after it has been moved to the target system. This framework is not a single event but a multi-stage approach, encompassing various testing types to ensure the migrated data meets all business and technical requirements.
This rigorous validation is essential for building trust in the new system. It moves beyond simple data-to-data comparison and tests how the data behaves within the new application’s context. By implementing a formal framework, you can systematically identify and rectify discrepancies, from corrupted records to broken business logic, before they impact live operations and erode user confidence.
Why This Practice is Essential
Without a structured testing framework, organisations are essentially flying blind, hoping that the data has transferred correctly. This is one of the most critical data migration best practices because it provides objective proof that the migration was successful. It confirms that data integrity is intact, application performance is acceptable, and the system is ready for business users, thereby preventing post-launch chaos and data-related financial losses.
For a care provider migrating to a new electronic patient record system, validation is paramount. The testing framework would include automated checks to ensure all patient identifiers and allergy information have been transferred without error. Crucially, it would also involve clinicians performing user acceptance testing (UAT) to confirm that care plans are displayed correctly and medication histories are fully intact and functional within the new interface.
"Data migration without rigorous validation is just data relocation. You've moved the problem, not solved it, and you won't know until it's too late."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Create Realistic Test Data: Develop test datasets that mirror the complexity and variety of your live production environment. Include edge cases and known data anomalies to ensure the new system can handle real-world scenarios.
- Automate Repetitive Validation: Use automated testing tools and scripts to perform high-volume validation tasks like record counts, checksums, and field-to-field data comparisons. This frees up human testers to focus on more complex functional and user acceptance testing.
- Involve End-Users Early: Engage business users, such as accountants or care coordinators, in User Acceptance Testing (UAT). Their domain expertise is invaluable for validating business rules and confirming that the migrated data supports their daily workflows correctly.
- Document All Test Cases and Results: Maintain a meticulous record of all test plans, scripts, outcomes, and defects. This documentation provides an auditable trail of validation activities and is crucial for effective project management and troubleshooting. This process is a key part of successful IT change management.
- Plan for Negative Testing: Deliberately test scenarios that are expected to fail. For example, attempt to process a transaction with incomplete data or violate a business rule. This helps confirm that the new system's error-handling and validation logic are working as designed.
5. Data Quality Management and Cleansing
Migrating flawed data to a new system is like moving into a pristine new office but bringing all the old clutter with you. Data quality management and cleansing is the practice of identifying, correcting, and ultimately preventing data inaccuracies before and during the migration process. It ensures that the data populating your new environment is reliable, accurate, and fit for purpose from the moment it arrives.
This process involves establishing clear quality standards and implementing procedures to scrub the source data of duplicates, inconsistencies, and incomplete records. It is a non-negotiable step because the value of any new system is directly tied to the quality of the data it holds. Poor data quality is a leading cause of migration failures, underscoring the importance of robust data quality management.

Why This Practice is Essential
This is one of the most critical data migration best practices because "garbage in, garbage out" is not just a cliché; it's a costly reality. Migrating poor-quality data can lead to failed business processes, inaccurate reporting, loss of customer trust, and significant post-migration clean-up costs that eclipse the initial project budget. For more insights on ensuring data integrity, consider these essential data quality best practices.
A practical example for an architectural practice would be cleansing its project database before moving to a new management system. This involves de-duplicating supplier contacts, standardising material specifications (e.g., ensuring "aluminium" is not also listed as "Al" or "alum."), and removing records for projects that were completed over a decade ago. This ensures the new system provides accurate project costing and reliable supplier information from day one.
"Investing in data cleansing before migration is not a cost; it's an investment in the long-term integrity and success of your business operations."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Establish Data Quality Metrics Early: Define what "clean" data means for your business before migration starts. Set measurable targets for accuracy, completeness, and consistency (e.g., 99.5% of client records must contain a valid postal code).
- Create Data Stewardship Roles: Assign clear responsibility for data quality. Nominate data stewards from different business departments (such as accounting or client management) who own the data and are empowered to make decisions about cleansing rules.
- Use Automated Data Quality Tools: Employ specialised software to automate the detection of duplicates, validation of addresses, and standardisation of formats. This drastically reduces manual effort and improves the accuracy of the cleansing process.
- Implement Checks at Multiple Stages: Do not treat cleansing as a one-off task. Perform quality checks during data extraction, transformation, and just before loading into the target system to catch any issues introduced during the process.
- Document All Cleansing Rules: Maintain a clear log of every decision made, rule applied, and data transformation performed. This documentation is vital for auditing, troubleshooting, and maintaining data governance post-migration.
6. Performance Optimisation and Resource Management
A data migration's efficiency is measured not just by its accuracy but also by its speed and minimal impact on business operations. Performance optimisation and resource management involve the strategic planning and execution of technical approaches to maximise migration throughput while carefully managing system resources. This practice focuses on tuning network bandwidth, using parallel processing, and allocating resources effectively to shrink the migration window.
For large-scale migrations, especially where downtime must be minimised, this is a critical discipline. It addresses the physical and virtual constraints of moving vast quantities of data, ensuring the process is completed within tight, pre-defined schedules without overloading source or target systems. This transforms a potentially disruptive, lengthy process into a swift and efficient technical operation.
Why This Practice is Essential
Without a focus on performance, large data migrations can cripple network infrastructure and bring daily operations to a standstill for unacceptable periods. This is one of the most important data migration best practices because it directly mitigates business disruption. By proactively identifying and resolving potential bottlenecks, organisations can execute complex migrations faster, reduce risk, and maintain service continuity.
Imagine a large professional services partnership with offices across the UK migrating its central document store to Microsoft 365. Instead of a single, slow transfer, they could use tools that allow for parallel uploads from each regional office directly to the cloud. By scheduling the bulk of the data transfer to occur overnight and over weekends, and throttling bandwidth during business hours, they can complete the migration within the planned timeframe without impacting employees' ability to work on client files.
"Ignoring migration performance is like trying to drain a lake with a bucket. The data will eventually get there, but the business may not survive the drought."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Identify and Address Bottlenecks Early: Use performance testing tools to simulate data transfer loads before the live migration. This helps pinpoint potential weak points in the network, storage I/O, or database processing capabilities so they can be addressed beforehand.
- Use Compression: Before transfer, compress data to significantly reduce its volume. This lowers network bandwidth requirements and can dramatically decrease transfer times, especially over wide area networks (WANs) or to cloud environments.
- Schedule Migrations During Low-Usage Periods: Plan the primary data transfer activities for off-peak hours, such as overnight or during weekends. This minimises the impact on system performance and end-users who rely on the source systems for daily tasks.
- Implement Parallel Processing: Where possible, divide large datasets into smaller segments and migrate them concurrently. Modern migration tools often support this, allowing you to leverage multiple processing threads or servers to accelerate the overall process.
- Utilise Bulk Loading Techniques: For database migrations, use the target system's native bulk loading utilities (e.g., SQL Server's BCP or Oracle's SQL*Loader). These tools are highly optimised for inserting large volumes of data far more efficiently than standard row-by-row SQL inserts.
7. Security and Compliance Throughout Migration
A secure data migration embeds robust security and compliance protocols into every phase of the project, from initial planning to post-migration validation. This practice involves a comprehensive strategy to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability while adhering to all relevant regulatory standards. It treats security not as a final checkbox but as an integral thread woven throughout the migration lifecycle, encompassing encryption, access control, and continuous monitoring.
In an era of increasing cyber threats and stringent regulations like GDPR, treating security as an afterthought is a critical error. This practice ensures that sensitive information is protected both at rest in the source and target systems and in transit during the transfer. It proactively addresses vulnerabilities, preventing data breaches, fines, and reputational damage that could undermine the entire migration effort.
Why This Practice is Essential
Failing to prioritise security and compliance can lead to catastrophic consequences, including severe data breaches, hefty regulatory penalties, and a complete loss of customer trust. Embedding these considerations from the start is one of the most critical data migration best practices because it safeguards your organisation’s most valuable asset—its data. It ensures that the migration not only succeeds technically but also reinforces your commitment to data protection.
For an accountancy firm handling sensitive client financial data, this is non-negotiable. During a server upgrade, data must be encrypted while being transferred across the network (in transit) and on the new server's hard drives (at rest). Access to the migration tools and data would be restricted to a small, named group of IT personnel, with all actions logged in an audit trail to meet compliance requirements for financial data handling.
"In data migration, security is not a feature you add at the end. It is the very foundation upon which a trustworthy and successful project is built."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Implement End-to-End Encryption: Ensure all data is encrypted both in transit (using protocols like TLS) and at rest (using database or storage-level encryption). This makes the data unreadable to unauthorised parties even if it is intercepted.
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege: Restrict access to migration tools, servers, and data to only those individuals who absolutely require it for their roles. This minimises the risk of both accidental and malicious data exposure.
- Maintain Detailed Audit Trails: Implement comprehensive logging for all migration activities. Audit logs should track who accessed what data, when, and what actions were performed, providing a clear record for security reviews and compliance checks. For a deeper understanding of securing your data, this guide on data security compliance offers essential insights.
- Conduct Pre-Migration Security Assessments: Before migration begins, perform a thorough security assessment of both the source and target environments. Identify and remediate any vulnerabilities to ensure the new system is secure from day one. Strong IT security policies are fundamental to this process.
- Use Data Masking for Non-Production Environments: When testing the migration process, use data masking or anonymisation techniques. This allows for realistic testing in development and staging environments without exposing sensitive, real-world customer or patient data.
8. Detailed Documentation and Knowledge Transfer
A data migration project's value extends far beyond the final data transfer. Detailed documentation and knowledge transfer ensure this value is sustained by systematically capturing every technical detail, process, and decision, then effectively passing that knowledge to the teams who will manage the new system. This practice involves creating a comprehensive library of documents, from architectural diagrams to operational runbooks, that serves as a permanent record of the project.
This process transforms temporary project knowledge into a lasting organisational asset. It ensures that when the migration team disbands, the business-as-usual (BAU) teams are not left trying to decipher a complex new environment. Proper documentation and a structured handover are critical for long-term system maintainability, troubleshooting, compliance, and planning for future upgrades.
Why This Practice is Essential
Without rigorous documentation, organisations create a "knowledge silo" within the migration team, which vanishes once the project concludes. This leads to inefficient operations, longer incident resolution times, and significant risks if key personnel leave. This is one of the most crucial data migration best practices because it safeguards the investment made in the migration, empowering operational teams to manage, maintain, and evolve the new system effectively from day one.
A practical example is creating a "runbook" for the new system. For a care provider, this document would detail the daily backup procedure for the new patient management system, provide step-by-step instructions for restoring a single patient record, and list emergency contacts for critical software and hardware support. This empowers the in-house IT team to manage the system confidently without having to rely on the original migration specialists.
"Documentation is a love letter to your future self and your colleagues. In a data migration, it’s the blueprint that prevents the future team from having to solve the same complex problems all over again."
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement this practice, your organisation should:
- Use Collaborative Platforms: Employ tools like Confluence, SharePoint, or even a well-organised Git repository. These platforms allow for real-time collaboration, version control, and easy access for all relevant stakeholders, from developers to support analysts.
- Create Standardised Templates: Develop consistent templates for different types of documentation, such as data mapping specifications, testing plans, and incident response procedures. This ensures all essential information is captured uniformly across the project.
- Assign Clear Responsibilities: Make documentation a defined task within the project plan. Assign specific individuals or roles the responsibility for creating, reviewing, and signing off on key documents to ensure accountability.
- Integrate Visuals: Use diagrams, flowcharts, and architectural maps to explain complex processes and system interdependencies. Visual aids are often far more effective than dense text for conveying how data flows and systems interact.
- Conduct Formal Handover Sessions: Schedule structured knowledge transfer workshops with the operational teams who will inherit the system. Use the documentation as a guide for these sessions, combining theoretical review with hands-on training and Q&A.
8-Key Data Migration Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Data Assessment and Planning | High – requires skilled analysts and detailed analysis | High – time-intensive and skilled personnel | Clear understanding of data and risks, accurate scoping | Large or complex migrations needing detailed planning | Reduces unexpected issues, enables budgeting accuracy |
| Robust Data Backup and Recovery Strategy | Medium – involves multiple backup systems and validation steps | High – additional storage and testing | Minimised data loss, fast rollback capability | Any migration with critical data integrity needs | Minimises data loss risk, supports compliance |
| Phased Migration Approach | Medium to High – requires phase coordination and validation | Medium – requires cross-team collaboration | Gradual migration with reduced risk and business continuity | Large-scale, mission-critical, or complex systems | Allows risk reduction, early wins, and course correction |
| Comprehensive Testing and Validation Framework | High – multi-layered testing and validation needed | High – requires skilled testers and tools | Verified data accuracy and functionality, reduced support issues | Migrations with strict data accuracy and business rule needs | Ensures data integrity, builds stakeholder confidence |
| Data Quality Management and Cleansing | High – extensive remediation and validation needed | High – business stakeholder involvement and tools | Improved data reliability, fewer post-migration issues | Migrations where data quality issues are significant | Enhances data usability, supports regulatory compliance |
| Performance Optimisation and Resource Management | High – requires technical expertise and tuning | Medium to High – specialised tools and testing | Faster migration, minimal system impact | Large volume or time-constrained migrations | Reduces migration time, lowers operational costs |
| Security and Compliance Throughout Migration | Medium to High – complex security and compliance measures | Medium to High – security tools and expertise | Protected sensitive data, regulatory adherence | Regulated industries or sensitive data migrations | Maintains trust, reduces legal risks |
| Detailed Documentation and Knowledge Transfer | Medium – needs continuous documentation upkeep | Medium – time and collaboration efforts | Long-term maintainability, knowledge retention | Any migration requiring ongoing support or future changes | Supports effective handover, reduces team dependency |
Partnering for a Successful Migration Journey
Navigating the complexities of data migration is one of the most critical IT undertakings a business can face. As we have explored, a successful project is not a single action but a symphony of carefully orchestrated best practices. From the foundational Comprehensive Data Assessment and Planning that maps your entire journey to the final Detailed Documentation and Knowledge Transfer that empowers your team post-migration, each step is integral to the project's overall success.
Adhering to these data migration best practices transforms a high-risk initiative into a strategic business advantage. By implementing a Phased Migration Approach, for example, a Wiltshire-based accountancy firm can move client financial data incrementally, ensuring that core services remain uninterrupted during tax season. Similarly, a care provider in Somerset can leverage a Comprehensive Testing and Validation Framework to verify that patient records are transferred with 100% accuracy, safeguarding data integrity and upholding its duty of care.
Synthesising Best Practices into a Cohesive Strategy
The true power of these guidelines emerges when they are integrated into a single, cohesive strategy. Think of them not as a checklist to be ticked off, but as interconnected pillars supporting the entire structure of your project.
- Proactive Defence: A Robust Data Backup and Recovery Strategy is your safety net, while stringent Security and Compliance Throughout Migration acts as your armour, protecting your sensitive information from threats at every stage.
- Quality and Efficiency: Proactive Data Quality Management and Cleansing ensures you are not migrating legacy issues, while Performance Optimisation and Resource Management guarantees your new system operates at peak efficiency from day one.
Mastering these concepts is not merely about avoiding downtime or preventing data loss; it is about unlocking the full potential of your new system. A flawlessly executed migration ensures that the business benefits you envisioned, such as improved scalability, enhanced security, or greater analytical capabilities, are realised without being compromised by a flawed implementation process.
Key Takeaway: A successful data migration is the result of meticulous planning, disciplined execution, and a holistic understanding of how each best practice influences the others. It is an investment in your organisation's future data infrastructure, ensuring it is secure, reliable, and fit for purpose.
Ultimately, your data is your organisation’s lifeblood. Protecting it during a period of significant change is paramount. The principles outlined in this article provide a robust framework for any business, whether in Dorset, Hampshire, or beyond, to de-risk the process and achieve a seamless transition. By embracing these data migration best practices, you can confidently modernise your systems, secure your digital assets, and position your organisation for future growth. The journey may be complex, but with the right preparation and expertise, the destination is well worth the effort.
Are you ready to ensure your next data migration is a seamless success? The expert team at SES Computers has over 30 years of experience helping businesses across the region with complex IT projects, offering the specialised knowledge and proactive support needed to navigate every challenge. Contact our local specialists today to discover how we can transform your migration into a strategic triumph.