10 Key Business Technology Trends for UK SMEs in 2025
In today's fast-paced market, staying ahead is not just an advantage; it's a necessity for survival and growth. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) across Dorset, Somerset, and other UK regions, particularly those in professional services like accountancy or care, harnessing the right technology is the key to unlocking new levels of efficiency and client value. The coming year promises a new wave of innovation, but navigating which advancements truly matter can be a significant challenge for busy decision-makers.
This article cuts through the noise to deliver a practical guide to the most impactful business technology trends set to shape the future. We move beyond buzzwords to provide a clear, actionable roadmap tailored for UK businesses. Inside, you will find detailed explanations of each trend, from integrating artificial intelligence to enhance client services to adopting robust, proactive cybersecurity frameworks that protect your sensitive data.
We will explore real-world examples and offer concrete implementation steps for each technology, helping you make informed decisions. This roundup is designed to help you optimise operations, strengthen compliance, and secure a decisive competitive edge. Let's explore the ten essential technologies poised to redefine your business strategy and prepare you for what's next.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are no longer futuristic concepts; they are foundational business technology trends actively reshaping industries. This trend involves integrating intelligent algorithms into core business operations to automate tasks, derive insights from data, and enhance decision-making. By learning from data patterns, AI systems can perform tasks that traditionally required human intellect. For a professional services firm, this could mean an AI tool that analyses thousands of legal contracts to identify key clauses, or a system for an accountancy practice that automates the categorisation of expenses with near-perfect accuracy.
This technology is pivotal for gaining a competitive edge. It allows businesses to move beyond reactive problem-solving to proactive, predictive strategies. For instance, AI can forecast cash flow for a financial advisory client, optimise resource allocation in a consultancy, and even predict client churn, enabling you to take preventative action. In client services, AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 support for routine queries, freeing up human advisors to handle more complex strategic issues. For a deeper dive into specific applications, explore how AI is shaping call centres in the coming years with the latest AI trends in call centers for 2025.
Key Statistics Driving Adoption
The rapid adoption and economic impact of AI are staggering, underscoring its importance for any forward-thinking organisation.
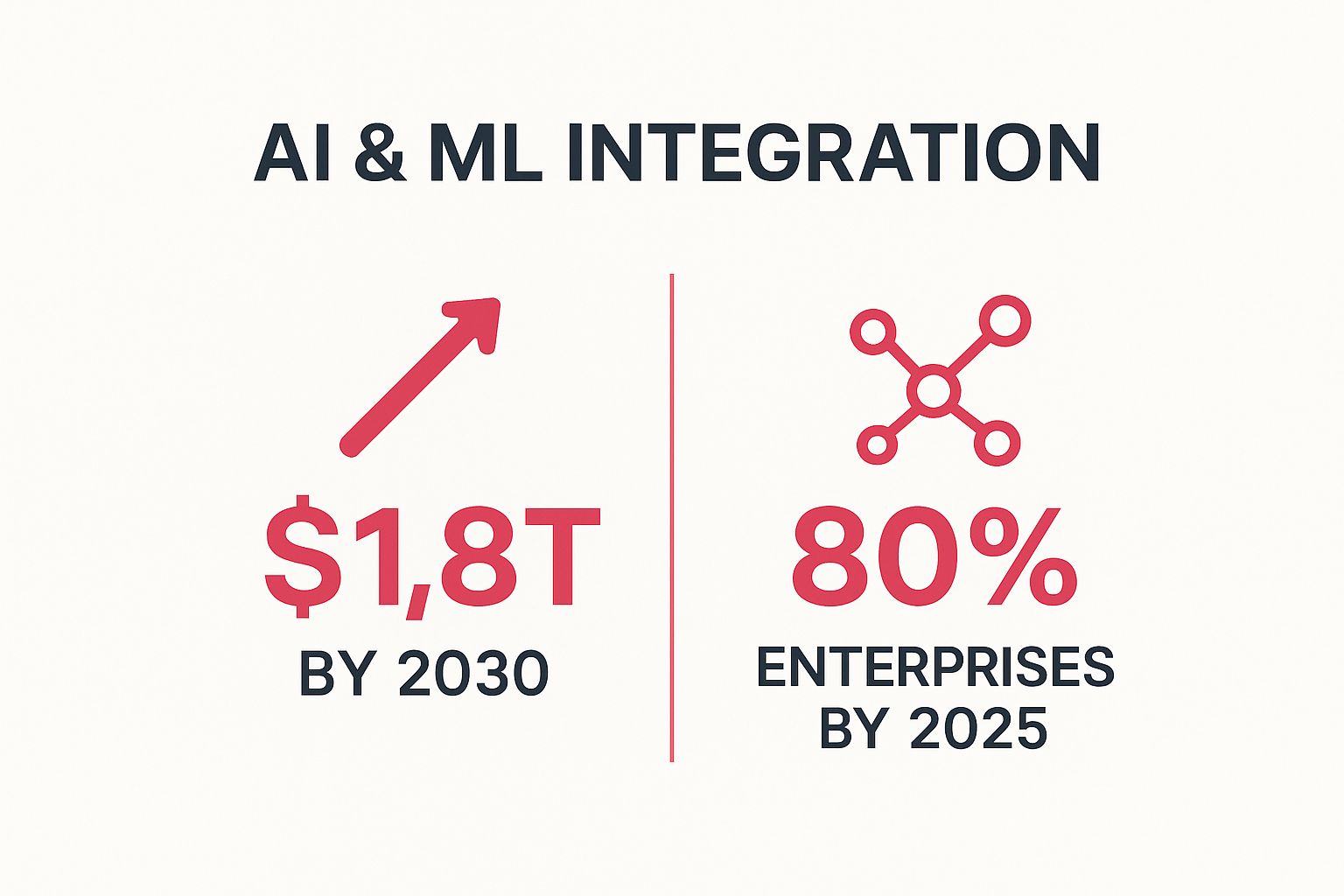
These figures highlight a clear trajectory: AI integration is becoming standard practice, generating substantial economic value and transforming how businesses operate.
How to Implement AI & ML
- Start Small: Begin with a focused pilot project. For example, an accountancy firm could pilot an AI-powered expense management tool for a small group of clients to demonstrate value and manage risk.
- Prioritise Data Quality: AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. Invest in data cleansing and governance before implementation.
- Foster Change Management: Train your team not just on the new tools but also on the new ways of working alongside AI.
- Partner with Experts: For initial projects, consider collaborating with a specialist AI vendor to leverage their expertise and accelerate deployment.
2. Cloud-First and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Adopting a cloud-first posture has become a defining business technology trend for modern organisations. This strategy involves prioritising cloud solutions for new IT projects and migrating existing infrastructure away from on-premise servers. A more advanced approach, the multi-cloud strategy, utilises services from two or more cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. This prevents vendor lock-in, optimises costs by selecting the best service for each workload, and enhances resilience through redundancy. For instance, a law firm might use a highly secure, specialised cloud for its case management system while using Microsoft Azure for its standard office productivity tools.

This strategic shift empowers businesses with unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and operational efficiency. Instead of purchasing and maintaining expensive physical hardware, companies can pay for computing resources as needed, scaling up during peak periods and down during quieter times. This is particularly beneficial for professional services firms, such as accountants, who experience seasonal demand during tax season. The cloud also facilitates secure remote work and collaboration, which is now a cornerstone of business continuity. Realising the full scope of these advantages is crucial for any business looking to compete, and you can explore the extensive cloud computing benefits for businesses to build a stronger case for adoption.
How to Implement Cloud Strategies
- Conduct a Cloud Readiness Assessment: Evaluate your current IT infrastructure, applications, and processes to identify opportunities and challenges for cloud migration.
- Prioritise Security and Compliance: Implement robust security controls, identity management, and data encryption. Ensure your chosen cloud provider meets industry-specific compliance standards, such as those relevant for solicitors or financial advisors.
- Plan a Phased Migration: Avoid a risky "big-bang" approach. Start by migrating less critical workloads, like a development environment or internal file sharing, to gain experience before moving core business applications.
- Invest in Cloud Skills: Train your IT team on cloud architecture, security, and management or partner with a managed service provider to fill expertise gaps.
- Utilise Cloud Management Platforms: For multi-cloud environments, use a centralised platform to monitor performance, manage costs, and automate processes across different providers.
3. Cybersecurity-by-Design and Zero Trust Architecture
As businesses embrace digital transformation, the traditional security model of a defensible network perimeter has become obsolete. This is where Cybersecurity-by-Design and Zero Trust Architecture emerge as critical business technology trends. This approach operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," assuming no user or device, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. It embeds security into the fabric of the IT infrastructure from the outset, rather than applying it as an afterthought.
This model is a paradigm shift from reactive defence to proactive security posture management. Instead of building a wall around your assets, you secure each individual resource and enforce strict access controls for every request. For a professional services firm, this means a partner working from a client site must re-authenticate to access every file, application, or database, just as they would if they were a new user. For businesses like accountants or care providers, this ensures sensitive client data is protected at every level, a crucial factor for compliance and trust.
Key Statistics Driving Adoption
The move towards Zero Trust is driven by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the dissolution of the traditional office environment.

These figures show that Zero Trust is no longer a niche concept but a mainstream strategy essential for mitigating risk and building a resilient organisation.
How to Implement a Zero Trust Model
- Start with Identity: Prioritise robust identity and access management (IAM). Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all systems without exception.
- Segment Your Network: Divide your network into smaller, isolated micro-segments to contain potential breaches and limit lateral movement by attackers.
- Enforce Least Privilege Access: Ensure users and applications have only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their specific roles. Regularly audit and revoke unneeded permissions.
- Invest in Continuous Training: Technology alone is not enough. Enhance your defences with ongoing IT security awareness training for your employees to create a security-conscious culture.
4. Low-Code/No-Code Development Platforms
The democratisation of software development is one of the most transformative business technology trends, driven largely by low-code/no-code (LCNC) platforms. This trend empowers non-technical staff, often called citizen developers, to build and deploy business applications using intuitive graphical interfaces, drag-and-drop components, and pre-built templates. Instead of writing complex code, users can design workflows and create custom tools, dramatically accelerating innovation. For example, an accountancy firm can build a bespoke client onboarding portal, or a care provider can create an application for tracking patient visits, all without relying on a dedicated IT department.
This approach is pivotal for agility and efficiency, allowing businesses to respond rapidly to changing needs. It bridges the gap between business requirements and technical implementation, enabling teams to solve their own problems. Platforms like the Microsoft Power Platform and Airtable allow users to create everything from simple data collection forms to sophisticated project management dashboards. This significantly reduces the IT backlog and fosters a culture of innovation across the organisation. For businesses keen on optimising their development overheads, exploring these platforms is essential. You can learn more about strategies for long-term savings in software development on sescomputers.com.
How to Implement Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
- Establish Governance: Create clear policies for what can be built, who can build it, and how applications are tested and secured to avoid uncontrolled 'shadow IT'.
- Start with Simple Processes: Begin by automating a low-risk, internal process, such as holiday requests or expense claims, to build confidence and demonstrate value.
- Provide Structured Training: Offer formal training on the chosen platform’s best practices, focusing on security, data management, and user experience design.
- Maintain an Application Inventory: Keep a central register of all applications created to ensure visibility, manage updates, and avoid redundant solutions.
5. Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing
The Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing represent a powerful convergence of business technology trends, transforming how organisations gather and act on real-time data. IoT involves a network of interconnected devices and sensors that collect and exchange information, while edge computing processes this data locally, close to its source, rather than sending it to a centralised cloud. This combination enables instant insights and automated responses, creating smarter, more efficient business operations.
This trend is critical for organisations that rely on immediate data for decision-making. For professional services, this could manifest in smart office buildings that optimise energy use based on occupancy, reducing overheads. In the care sector, IoT sensors can monitor vulnerable clients at home, sending instant alerts to care providers in case of a fall or other emergency, with edge computing ensuring the alert is processed immediately without relying on internet latency. This approach moves businesses from reactive analysis to proactive, automated control over their physical environments.
Key Statistics Driving Adoption
The growth of IoT and its partnership with edge computing is creating a new frontier for data-driven operations and automation across industries.
- Global IoT Market Size: The global IoT market is projected to reach over £1.1 trillion by 2026, demonstrating its massive scale and investment appeal.
- Edge Computing Growth: The edge computing market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 37% between 2021 and 2028, driven by the need for low-latency processing.
- Device Proliferation: It is estimated there will be more than 29 billion connected IoT devices worldwide by 2030, highlighting the ubiquity of this technology.
These figures illustrate a clear shift towards decentralised intelligence, where data is processed at the source for maximum speed and relevance.
How to Implement IoT & Edge Computing
- Define a Specific Use Case: Start by identifying a clear, high-impact problem to solve, such as monitoring high-value assets in an office or automating environmental controls in a care home.
- Prioritise Security: From the outset, implement robust security protocols for all connected devices to protect against data breaches and unauthorised access.
- Plan for Connectivity: Assess your bandwidth and network infrastructure. Ensure it can support the data volume from your IoT devices, especially in rural areas of Dorset or Somerset.
- Develop a Data Strategy: Establish clear guidelines for how IoT data will be collected, processed, stored, and managed to ensure its integrity and usefulness.
6. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a significant business technology trend that allows organisations to automate high-volume, repetitive digital tasks. Unlike physical robots, RPA utilises software "bots" that mimic human actions to interact with digital systems. These bots can log into applications, enter data, calculate, and complete rule-based tasks, all without human intervention. For a professional services firm like an accountancy practice, an RPA bot can automatically download bank statements, extract transaction data, and populate it into accounting software, saving hundreds of hours of manual work per month.
This technology is transformative for businesses looking to streamline operations and reduce costs. By automating mundane processes like invoice processing, data entry, or client record updates, RPA frees up skilled employees to focus on higher-value activities that require strategic thinking, client interaction, and complex problem-solving. This not only boosts productivity but also enhances employee satisfaction by eliminating tedious work. Platforms from leaders like UiPath and Automation Anywhere are making this powerful technology more accessible to small and medium enterprises.
Key Statistics Driving Adoption
The growth and impact of RPA are compelling, demonstrating its established role in modern business operations and its potential for substantial returns on investment.
These figures confirm that RPA is not a fleeting trend but a core component of digital transformation, offering tangible benefits in efficiency and cost reduction.
How to Implement RPA
- Identify High-Impact Processes: Begin by auditing tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and high-volume. For a solicitor's office, this could be generating standard client engagement letters or completing property search forms.
- Standardise Before Automating: Ensure the target process is optimised and standardised. Automating an inefficient process only magnifies its flaws.
- Start with a Pilot Project: Launch a small-scale pilot to demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) and build internal support before a wider rollout.
- Establish Governance and Monitoring: Implement clear governance policies for bot management, security, and performance monitoring to maintain control and ensure reliability.
- Train Your Team: Prepare your staff for the change by training them to work alongside bots and manage the new automated workflows.
7. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Business
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are immersive technologies that are moving from consumer entertainment into practical business applications. This business technology trend involves overlaying digital information onto the real world (AR) or creating entirely digital environments (VR). These tools are transforming core operations like training, product visualisation, and client engagement, offering innovative ways to interact with information and physical spaces.
This trend is crucial for businesses aiming to create more impactful and efficient processes. For example, architects and engineering firms can use VR to walk clients through a virtual model of a proposed building, allowing for immediate feedback and design changes before construction begins. In the care sector, VR can be used for empathy training, allowing staff to experience the challenges faced by patients with specific conditions. In legal services, AR could overlay case evidence onto a real-world environment during trial preparation.
Key Applications Driving Adoption
The practical applications of AR and VR are expanding rapidly across industries, providing tangible returns on investment and enhancing operational capabilities.
These use cases demonstrate that AR and VR are powerful tools for solving real-world business challenges, from upskilling employees to creating unforgettable client experiences.
How to Implement AR & VR
- Identify a Specific Use Case: Start by focusing on a single, high-impact area, such as virtual onboarding for new remote employees or creating an interactive AR presentation for client pitches.
- Choose User-Friendly Hardware: Select AR/VR devices that are intuitive and comfortable for your team or clients to use, minimising the learning curve.
- Prioritise High-Quality Content: The success of AR/VR hinges on the quality of the digital content. Invest in realistic and useful simulations or visualisations.
- Measure the Return on Investment (ROI): Track specific metrics to justify the investment. This could include reduced training times, higher client engagement rates, or faster project approval cycles.
8. Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) are moving far beyond their origins in cryptocurrency to become a transformative business technology trend. This technology utilises a decentralised, immutable digital ledger to record transactions across many computers, ensuring that any record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network. This creates unprecedented levels of transparency, security, and traceability for business processes.
The application of blockchain is proving pivotal for industries where trust and provenance are paramount. For professional services, this translates into smart contracts that automatically execute terms of an agreement—such as releasing payment upon completion of a project milestone—reducing administrative overhead and disputes. A law firm could use it to create an unalterable chain of custody for digital evidence, while an accountancy practice could use it for triple-entry bookkeeping, providing a tamper-proof record shared between a business, its customers, and its suppliers. One significant application is the adoption of secure blockchain payment solutions, which can reduce transaction costs and settlement times.
Key Statistics Driving Adoption
The growing investment and projected market size for blockchain technology underscore its increasing importance and potential for delivering significant business value.
These figures illustrate that organisations are increasingly recognising blockchain's capacity to streamline operations, enhance security, and create new business models.
How to Implement Blockchain & DLT
- Identify a Specific Use Case: Don't adopt blockchain for its own sake. Focus on a clear problem it can solve, such as supply chain transparency, intellectual property verification, or creating smart contracts for professional services.
- Start with a Private or Consortium Blockchain: Public blockchains are not always necessary. A private blockchain controlled by your organisation or a consortium blockchain shared with trusted partners offers more control and privacy for business applications.
- Partner with Platform Providers: Leverage established platforms like IBM Blockchain or R3's Corda to accelerate development and avoid building the underlying infrastructure from scratch.
- Educate Stakeholders: Ensure all stakeholders, from your internal team to external partners, understand the benefits and operational changes associated with implementing DLT.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Stay informed about the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology, particularly concerning data privacy and financial transactions, to ensure your implementation is compliant.
9. 5G and Advanced Connectivity Solutions
The rollout of 5G represents a monumental leap in wireless communication, far exceeding the incremental improvements of previous generations. This business technology trend provides ultra-fast data speeds, significantly reduced latency, and the capacity to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously. It moves beyond simply faster mobile browsing, acting as a catalyst for transformative applications like real-time data analytics, large-scale Internet of Things (IoT) deployments, and immersive augmented reality (AR) experiences for training and client support.
This enhanced connectivity is critical for businesses aiming to operate at the edge of innovation. For professional services firms, this means a consultant can download and analyse a massive client dataset in seconds while on-site, or a surveyor can transmit high-definition drone footage from a remote location in real time. For UK businesses, this opens doors to smarter operations, from an accountancy firm securely accessing cloud data instantly to a care provider using reliable telehealth services with crystal-clear video quality.
Key Statistics Driving Adoption
The rapid expansion and economic potential of 5G underscore its role as a foundational infrastructure for future business growth and innovation.
- The global 5G services market is projected to grow from £53 billion in 2022 to £2.5 trillion by 2030, demonstrating explosive demand.
- 5G can support up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometre, a 10x increase over 4G, making it essential for IoT.
- It offers latency as low as 1 millisecond, enabling real-time control over remote operations and machinery.
These figures illustrate that 5G is not just an upgrade but a core enabler of the next wave of digital transformation, creating new business models and revenue streams.
How to Implement 5G & Advanced Connectivity
- Assess Local Availability: Begin by verifying 5G network coverage and quality from major UK carriers like EE, Vodafone, or O2 in your specific business locations across Dorset, Somerset, or Wiltshire.
- Identify High-Impact Use Cases: Pinpoint specific operations that would benefit most from low latency or high bandwidth, such as remote client consultations, large data transfers for financial modelling, or AR-assisted field service.
- Plan for Infrastructure Upgrades: Ensure your hardware, including routers, modems, and employee devices, is 5G-compatible to fully capitalise on the network's capabilities.
- Prioritise Security: The increased connectivity expands your network's attack surface. Implement robust security protocols and consider a private 5G network for sensitive industrial or data-heavy applications.
10. Sustainable Technology and Green IT
Sustainable Technology, often called Green IT, is a critical business technology trend focused on minimising the environmental footprint of IT operations. This involves adopting energy-efficient hardware, utilising renewable energy sources for data centres, and integrating circular economy principles to reduce e-waste. As organisations like Microsoft pursue carbon-negative goals, this trend moves from a corporate social responsibility talking point to a core operational strategy, enhancing brand reputation and long-term resilience.
This approach is pivotal for future-proofing a business against regulatory changes and shifting consumer expectations. Green IT not only reduces operational costs through lower energy consumption but also aligns your organisation with the values of environmentally conscious clients and partners. For a professional services firm, this could mean choosing a cloud provider that runs on 100% renewable energy or implementing a device lifecycle policy that prioritises repair and refurbishment over replacement. The integration of artificial intelligence is also transforming green initiatives, with leading sustainability software leveraging AI to enhance data analysis and reporting for environmental impact.
Key Statistics Driving Adoption
The push towards sustainability is backed by significant data, highlighting both environmental necessity and economic opportunity.
Globally, data centres consume an estimated 200 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity each year, an amount greater than the national energy consumption of some countries. Adopting Green IT practices can reduce this figure by optimising energy use and shifting to renewable sources. This move is not just ecological but also economical, as energy costs are a major operational expense for any business with a digital presence.
These figures underscore the urgency and benefit of integrating sustainability into your technology strategy, transforming a cost centre into a source of efficiency and value.
How to Implement Sustainable Technology
- Conduct an Energy Audit: Start by assessing your current IT energy consumption to identify key areas for improvement, from servers to individual workstations.
- Prioritise Cloud Computing: Migrate services to the cloud to reduce your on-premise hardware footprint. Major cloud providers often operate highly efficient, renewably powered data centres.
- Choose Sustainable Vendors: Partner with hardware and software suppliers who demonstrate a strong commitment to environmental standards and circular economy practices.
- Set Measurable Goals: Establish clear, quantifiable sustainability targets, such as reducing your IT carbon footprint by a specific percentage, and track your progress.
Top 10 Business Tech Trends Comparison
| Technology | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration | High – requires technical expertise and data quality | Significant initial investment, skilled staff | Automation, enhanced decision-making, personalisation | Process automation, predictive analytics | Increased efficiency, reduced errors, 24/7 operation |
| Cloud-First and Multi-Cloud Strategies | Moderate to high – requires planning and management | Ongoing subscription costs, cloud expertise | Scalability, cost optimisation, reliability | Infrastructure modernisation, workload migration | Flexibility, reduced infrastructure costs, disaster recovery |
| Cybersecurity-by-Design and Zero Trust Architecture | High – complex integration and cultural change | Specialised security skills, higher upfront costs | Enhanced security, continuous verification | Security-sensitive environments, remote work | Reduced attack surface, regulatory compliance, real-time threat response |
| Low-Code/No-Code Development Platforms | Low to moderate – user-friendly but requires governance | Lower development costs, some training needed | Faster app development, empowered non-technical users | Rapid prototyping, business user-driven apps | Faster delivery, reduced IT dependency, cost-effective |
| Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing | High – device management and network complexity | High infrastructure investment, security focus | Real-time insights, predictive maintenance | Industrial automation, supply chain tracking | Improved efficiency, real-time decisions, cost reduction |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Moderate – process standardisation needed | Moderate setup costs, bot management skills | Automates repetitive tasks, cost savings | Rule-based repetitive processes | Quick ROI, accuracy improvement, 24/7 operations |
| Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) | High – hardware and content development costs | Significant investment in devices and training | Enhanced engagement, immersive training | Employee training, product visualisation | Better visualisation, reduced costs, remote collaboration |
| Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies | High – technical complexity and regulatory issues | Significant expertise, energy/resource intensive | Transparency, fraud reduction | Supply chain, secure data sharing | Decentralisation, immutable records, enhanced security |
| 5G and Advanced Connectivity Solutions | High – infrastructure upgrades required | High infrastructure costs, device compatibility | Faster connectivity, massive device support | IoT deployments, real-time analytics | Low latency, high speed, new business opportunities |
| Sustainable Technology and Green IT | Moderate to high – requires sustainability integration | Higher initial investment, monitoring tools | Reduced environmental impact, cost savings | Energy management, green supply chains | Improved reputation, long-term cost savings, compliance |
Your Next Move: Turning Tech Trends into Business Triumphs
Navigating the landscape of emerging business technology trends can feel like trying to hit a moving target. However, as we have explored, these advancements are not just fleeting novelties; they are foundational pillars for the future of commerce. From the predictive power of Artificial Intelligence and the scalability of multi-cloud strategies to the democratic innovation offered by low-code platforms, each trend represents a powerful opportunity. The common thread weaving through them all is the drive for greater efficiency, enhanced security, and deeper client engagement.
For small and medium-sized businesses, particularly professional services firms like accountants or care providers in Dorset, Somerset, Wiltshire, and Hampshire, the message is one of strategic adoption, not overwhelming revolution. The goal is not to implement all ten technologies at once. Instead, it is to identify the specific operational bottlenecks or strategic goals where technology can deliver the most significant impact.
From Insight to Implementation: Your Action Plan
The transition from understanding these trends to leveraging them requires a deliberate and measured approach. Rather than seeing this as a single, monumental project, view it as a series of strategic steps tailored to your unique circumstances.
- Conduct a Technology Audit: Begin by evaluating your current technology stack. Where are the inefficiencies? What systems are outdated or creating security vulnerabilities? A clear understanding of your starting point is essential before you can map out a route forward. For example, a legal practice might realise its on-premise server is a single point of failure, making a cloud-first strategy a high-priority initiative.
- Prioritise Based on Business Impact: Rank your challenges and opportunities. Is your primary concern improving client data security? Then Cybersecurity-by-Design and a Zero Trust framework should be at the top of your list. Are you looking to streamline repetitive administrative tasks to free up your team? Then Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a logical starting point.
- Start Small and Scale: Select one or two trends that promise the highest return for your specific needs. Pilot a project with a defined scope and clear metrics for success. A small accountancy firm could pilot a low-code app to automate client onboarding paperwork, measuring success by the reduction in administrative hours and improvement in client satisfaction, before rolling it out more widely.
The True Value of Technological Advancement
Ultimately, mastering these business technology trends is about more than just modernising your toolkit. It is about building a more agile, resilient, and competitive organisation. It is about empowering your team to focus on high-value work, securing your operations against an evolving threat landscape, and delivering the seamless, responsive service that today’s clients expect. By taking a proactive, informed, and strategic approach, you can transform these powerful technological shifts from abstract concepts into tangible business triumphs, securing your organisation's success for years to come.
Ready to turn these technological trends into your competitive advantage? The experts at SES Computers specialise in helping businesses across Dorset, Somerset, and the South West implement robust cybersecurity, scalable cloud solutions, and bespoke IT strategies. Visit SES Computers to discover how our tailored support can help your business thrive in the digital age.