Robust Security for WiFi Your Business Can Trust
Getting your Wi-Fi security right doesn't start with expensive, enterprise-level kit. It begins with tackling the most common and easily fixed vulnerabilities – the things attackers look for first. We're talking about changing default router passwords, switching off risky "convenience" features, and making sure your admin access is properly locked down. These foundational steps are your strongest first line of defence.
Building Your First Line of Defence
The bedrock of solid Wi-Fi security is a methodical process of eliminating the low-hanging fruit. I’ve seen it time and time again: businesses, from small accountancy firms to local high street shops, unknowingly leave their digital front door wide open because of a few simple configuration mistakes.
Fixing these initial weaknesses is the single most impactful thing you can do. To truly build a robust defence, it helps to have a good grasp of network security fundamentals. Think of this initial setup as the essential groundwork; everything else you do to secure your network will be built on top of it.
Secure Your Router's Administrator Access
If you do only one thing, make it this: change your router's default administrator login details. Routers are shipped from the factory with generic usernames and passwords like "admin" and "password," which are all documented online for anyone to find. Leaving them as they are is the digital equivalent of leaving the keys in your office front door.
A practical example of this risk is a small marketing agency I worked with. An attacker scanned their public IP address, found the login page for their off-the-shelf router, and guessed the password ("admin") on the first try. Within minutes, the attacker had redirected the company’s website traffic to a malicious page.
An attacker with admin access to your router has complete control. They can redirect your internet traffic, spy on activity, change passwords, and disable every other security measure you have. It is the absolute number one entry point you need to secure.
For any professional environment, a strong, unique password is non-negotiable. I strongly recommend using a password manager to generate and store a long, complex credential for your router's admin panel, for example, something like £5b-p9!Tz-K&q7*R. This one action immediately boosts your security.
This infographic lays out the core process for building that initial Wi-Fi defence.
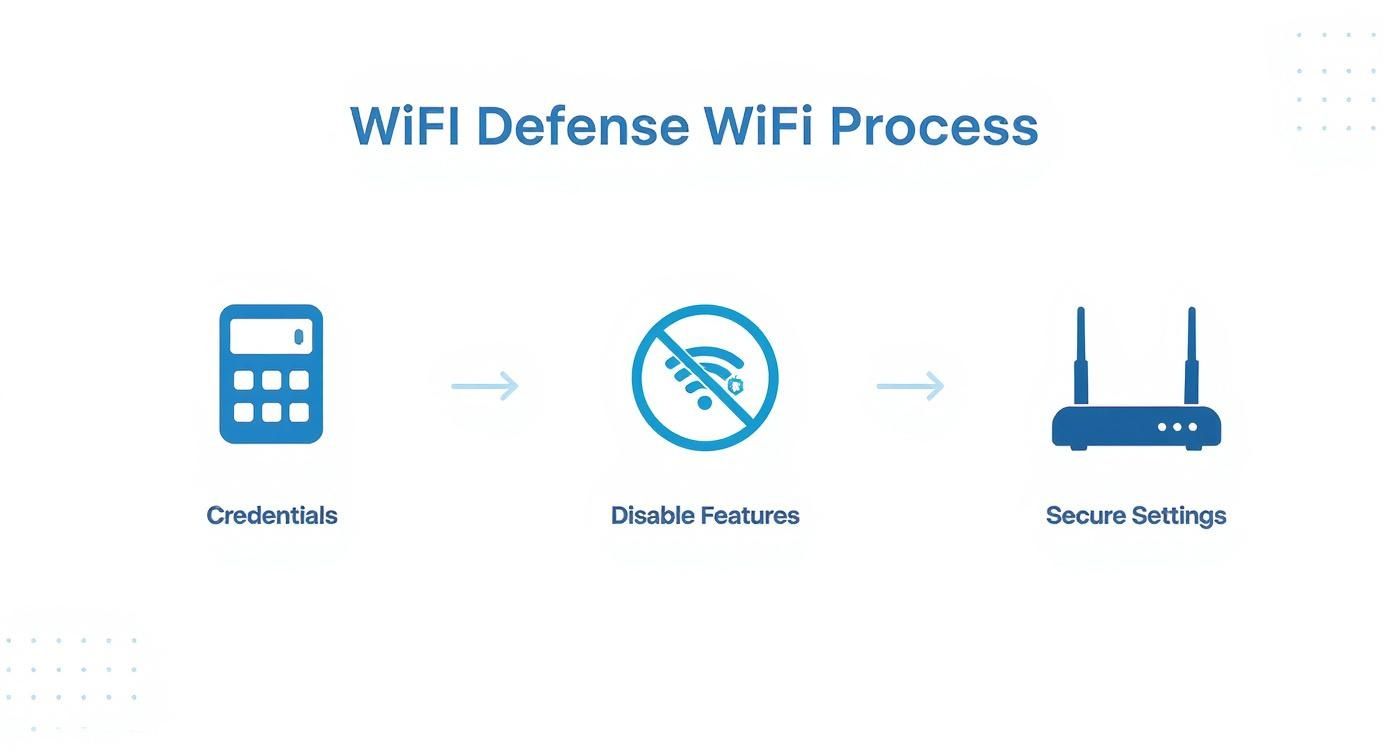
As you can see, it all comes back to securing credentials, disabling risky features, and getting your core settings right. These are the pillars of a solid security foundation.
Disable Unnecessary and Insecure Features
Modern routers often come packed with features designed for convenience, but some of them create unacceptable security risks in a business setting. The two main culprits are Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) and Universal Plug and Play (UPnP). They make it easier to connect new devices, but they also create backdoors that can be exploited.
Take WPS, for example. It uses a short PIN that can be cracked with brute-force tools in just a few hours. Once cracked, an attacker has your main Wi-Fi password and full network access.
Similarly, UPnP is a huge liability. It allows devices on your network to automatically open ports in your firewall, essentially punching holes in your defences. For instance, a compromised smart TV or printer in your reception area could use UPnP to expose your entire internal network to the internet without you ever knowing.
You should log into your router's administrative interface and disable both WPS and UPnP immediately. For businesses needing more robust and secure connectivity, it's often worth looking into dedicated https://www.sescomputers.com/news/business-broadband-solutions/ that come with better security controls from the start.
Essential Router Security Settings Comparison
To put this into practice, it's helpful to see a direct comparison of a typical, out-of-the-box router setup versus one that's been properly secured. Many devices ship with settings prioritising ease of use over security.
| Security Feature | Default (Insecure) Setting | Recommended (Secure) Setting | Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Admin Password | "admin" or "password" | A long, complex, unique password | Prevents unauthorised administrative access to the router. |
| WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) | Enabled | Disabled | The WPS PIN is notoriously easy to crack via brute-force attacks. |
| UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) | Enabled | Disabled | Prevents insecure devices from automatically opening ports in your firewall. |
| Remote Administration | Enabled | Disabled | Stops attempts to access your router’s settings from outside your local network. |
By making these simple but critical adjustments, you fundamentally change your router from a point of weakness into a strong gatekeeper for your network. It's the difference between an open door and a locked one.
Deploying Advanced Encryption and Authentication
Once you've sorted out your router's basic settings, the next crucial job is making the data flying through the air completely unreadable to anyone snooping around. This is all down to encryption, and the standard you pick is the difference between genuine protection and just a false sense of security.

For any business today, WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3) is the only real option. It’s non-negotiable, especially if you handle any kind of client or financial information. It directly addresses some serious weak spots in the older WPA2 standard, giving you much better protection against password-guessing attacks. Crucially, it also means that even if someone did manage to capture your network traffic, they couldn't go back and decipher data that was sent earlier.
Making the switch is usually quite simple on most modern business-grade routers. Just log in, head to the wireless security settings, and you'll likely see a dropdown menu for the security mode. The goal is to select WPA3. You might also spot a 'WPA2/WPA3' transitional mode—this is a handy option that provides backwards compatibility for any older devices on your network that can't handle the latest standard.
Choosing Between WPA3 Personal and Enterprise
So, which flavour of WPA3 do you need? This really comes down to the size of your business and how tight you need your security to be. While both give you powerful encryption, they approach user authentication in completely different ways. Getting this right is fundamental.
Here’s how they stack up:
-
WPA3-Personal: This is your go-to for small offices. It uses a single pre-shared key (PSK)—what everyone calls the Wi-Fi password—that the whole team uses to connect. It’s easy to manage and works perfectly for a small, trusted group, like a startup with fewer than ten people.
-
WPA3-Enterprise: This is the gold standard for larger businesses or any organisation that needs to control who can access what. Instead of one shared password, it uses the IEEE 802.1X protocol. This means every user gets their own unique login (a username and password), giving you far greater security and control.
For many businesses, that extra security layer of individual logins isn't just a 'nice-to-have'; it's essential. This is where WPA3-Enterprise really proves its worth, building a much more accountable and secure network.
A Practical Example: WPA3-Enterprise in Action
Think about a local law firm. They’re dealing with highly confidential case files and personal data every single day. Using a single shared password (WPA3-Personal) would be a massive risk. If an employee leaves, the password for the entire network has to be changed and passed around to everyone else—a process that’s both clunky and easily forgotten.
By setting up WPA3-Enterprise, the firm can link its Wi-Fi network to a RADIUS server.
This setup gives each solicitor, paralegal, and member of the admin staff their own unique login for the Wi-Fi. When someone leaves the firm, their individual network access can be switched off instantly, without affecting anyone else. It also creates a clear audit trail of who accessed the network and when—vital for data security and for meeting compliance rules like GDPR.
This level of control isn't just for big corporations. Any professional services business—accountants, financial advisers, or medical clinics—stands to benefit hugely from this kind of individual authentication.
The Role of Multi-Factor Authentication
If you want to take security to the next level, you can pair WPA3-Enterprise with extra verification methods. It’s the same idea as using a code from your phone to log into your email, but applied to your Wi-Fi network. This simple step adds a powerful barrier against anyone trying to get in who shouldn't be.
Adding this extra check means that even if a user's password was somehow compromised, an attacker still couldn't get onto the network without that second piece of verification. For instance, an employee would enter their password, then receive a push notification on their company mobile to approve the connection. If you want to dive deeper into the mechanics, you can learn more about what multi-factor authentication is and how it strengthens your defences. It's this combination of strong encryption and robust authentication that turns your wireless network into a much tougher target.
Segmenting Your Network to Contain Threats
Putting every device in your business—from employee laptops and guest smartphones to the smart coffee machine in the break room—onto one single, flat network is asking for trouble. It creates a digital free-for-all where one compromised device can quickly escalate into a company-wide crisis. Proper security for wifi isn't just about strong passwords; it's about building digital walls to contain threats. We call this network segmentation.

The idea is simple but powerful: you isolate different types of network traffic from each other. That way, if one area is breached, the attacker is trapped and can't move sideways to infect the rest of your systems. Think of it like the fire doors in a building—they stop a small fire in one room from burning down the entire structure.
Creating a Secure Guest Network
The easiest and most immediate step you can take is to set up a dedicated Wi-Fi network for your visitors. Any modern business-grade router will have a 'Guest Network' feature, and activating it is usually just a matter of ticking a box in the settings. This instantly walls off your clients, suppliers, and any other visitors from your core business network.
But don't stop there. Simply turning on the guest network isn't enough. There's a critical setting you need to enable called client isolation.
When this is switched on, it prevents devices connected to the guest network from seeing or communicating with each other. This is absolutely crucial. It stops a visitor's potentially malware-riddled laptop from sniffing around for other vulnerable guest devices. Everyone gets a safer connection.
Imagine a local coffee shop's free Wi-Fi. Without client isolation, a hacker could sit in the corner and use the public network to probe other customers' laptops for weaknesses. By enabling isolation, the café owner puts each user into their own private bubble, making them invisible to everyone else on the same network.
It’s a simple toggle that dramatically improves the security of your public Wi-Fi without any real effort.
Using VLANs for Deeper Segmentation
For much finer control over your main business network, you need to step up to Virtual Local Area Networks, or VLANs. A VLAN lets you chop up your physical network into multiple, separate virtual networks that all run on the same hardware. It’s a seriously effective way to enforce separation between different teams and functions in your business.
You can slice and dice your VLANs in whatever way makes sense for your company. Some common strategies I've seen work well include:
- By Department: Give Finance, Sales, and Operations their own separate VLANs. This ensures a compromised PC in the sales team can't directly access sensitive financial servers.
- By Device Type: Shove all your IoT (Internet of Things) gadgets—smart thermostats, security cameras, printers—onto their own dedicated VLAN.
- By Security Level: You might create a high-security VLAN for your critical servers and another for general employee workstations, then use strict firewall rules to manage exactly what can pass between them.
The true value of VLANs really clicks when you start thinking about the weakest links in your network.
Isolating Insecure IoT Devices
The explosion of connected "things" has opened up a whole new world of security risks. So many IoT devices are built with flimsy, afterthought security and almost never get updated, making them a prime target for attackers. In a recent security investigation, a smart bed was found to have a backdoor allowing engineers full remote control—and a potential gateway to everything else on the home network.
Now, apply that to your office. Imagine your smart security cameras are on the same network as your file server. If an attacker compromises one of those cameras, they have a direct line of sight to your most critical business data.
By placing all IoT devices on their own isolated VLAN, you effectively put them in a digital quarantine. Even if an attacker compromises a camera, they’re trapped. They can’t see or access your confidential client records or financial data sitting safely on a different network segment. This containment strategy is a cornerstone of modern network security, built on the realistic assumption that breaches will happen—the goal is to ensure they don't become catastrophic.
Keep Your Guard Up with Proactive Management
Securing your business Wi-Fi isn't a one-time job. You can't just set it up and walk away. It's a continuous process of staying alert and keeping things maintained, because the digital threats we face are always evolving. What's secure today might be vulnerable tomorrow.
The only real way to keep your network safe for the long haul is to build security habits into your daily and weekly operations. It’s all about shifting your mindset from reactive to proactive. Instead of scrambling to fix a problem after a breach, you’ll be prepared, staying one step ahead of potential threats. Think of it as essential servicing for your digital storefront – you wouldn't skip an oil change on your company vehicle, and this is no different.
Don't Skip the Firmware Updates
Your router’s firmware is its brain. It’s the software that runs everything, from connecting devices to enforcing your security rules. Manufacturers are constantly finding and fixing security holes in this software, releasing updates to patch them. Ignoring these updates is one of the easiest, and most common, ways businesses expose themselves to risk.
A practical example is the "VPNFilter" malware which specifically targeted routers with outdated firmware. Thousands of small businesses were affected because they had failed to apply a simple security patch released months earlier, allowing attackers to intercept traffic and steal credentials.
Thankfully, most modern business-grade routers can update themselves automatically. If you have that option, turn it on. If not, you need to get into the habit of checking for updates manually at least once a month. This simple step can slam the door shut on a whole category of common attacks.
A Practical Maintenance Checklist for Your Business
You don’t need a complicated, enterprise-level plan to stay on top of things. For most small and medium-sized businesses, a simple, consistent schedule is all it takes to make a huge difference.
Here’s a straightforward checklist you can adapt:
- Quarterly Password Rotation: Every three months, change your main Wi-Fi password. This is crucial for flushing out access from former employees, contractors, or anyone who might have got hold of the password over time.
- Bi-Annual Admin Credential Review: Change the router’s administrator password every six months. This password is the master key to your entire network, so it needs to be protected fiercely.
- Monthly Connected Device Audit: Once a month, log in to your router and look at the list of connected devices. Do you recognise every single one? If you see a device name or MAC address that’s unfamiliar, it’s a red flag that needs investigating immediately.
- Firmware Check (If Manual): As mentioned, if your router doesn't do it for you, set a monthly reminder to check for and install the latest firmware.
This whole routine takes very little time but delivers a massive return on investment when it comes to keeping your network secure.
When you make these actions a habit, you're building what security pros call 'operational resilience'. It means your security isn't just a one-off project; it’s baked into the way you do business.
Keep an Eye Out for Suspicious Activity
Beyond the scheduled maintenance, a truly proactive approach involves actively looking for signs of trouble. Your router keeps a log of everything that happens on your network. While these logs can seem a bit technical at first, learning to spot oddities is a skill worth developing.
What should you look for? Things like a sudden spike in failed login attempts to your admin portal could mean someone is trying to brute-force their way in. Repeated connection attempts from a device you don't recognise are also a major warning sign.
Many newer routers and access points let you set up alerts for specific events. One of the most powerful is an alert for when a new, previously unseen device connects to your network. This gives you a real-time heads-up about potential intruders, allowing you to act right away instead of finding out about a breach weeks or months down the line. For example, getting an email alert at 2 AM that a new phone has joined your office Wi-Fi is an immediate signal to investigate.
For businesses wanting to take this a step further, it's worth exploring some of the best network monitoring tools on the market. These platforms can automate much of this work, giving you deeper insights and smarter alerts to help you maintain constant vigilance over your network’s health.
Controlling Access and Mitigating Threats
Once you’ve got your encryption and network segmentation sorted, it’s time to get more granular. We need to control precisely who and what can connect to your business Wi-Fi. This is where we move beyond broad-stroke policies and start creating specific rules to govern access, building a much tougher defence against both casual and determined attackers.
Think of these measures as your network's digital bouncer. They check credentials and intentions at the door, filtering out unwanted connections and blocking shady activity before it ever gets a foothold. It’s all about shrinking your attack surface.
Add a Layer with MAC Address Filtering
A straightforward way to create an extra hurdle for intruders is to use MAC address filtering. Every single device that can connect to a network—from a laptop to a smart TV—has a unique hardware identifier called a Media Access Control (MAC) address. By enabling MAC filtering on your router, you can create an exclusive "allow list" of approved devices.
If a device’s MAC address isn't on your pre-approved list, the router simply won't let it connect. End of story. For instance, a small consultancy with five employees could create an allow list containing only the MAC addresses of their five company-issued laptops. This would prevent staff from connecting personal mobiles or an unknown device from ever joining the network.
Now, is it foolproof? No. A skilled attacker can "spoof" or clone an approved MAC address. But it's brilliant at stopping casual snoops or employees trying to connect personal, unmanaged devices to the main business network. For a smaller office, building this list is a quick job that instantly makes an attacker’s life harder.
Implement a Robust Firewall Policy
Your router's built-in firewall is one of the most powerful tools in your security arsenal. It acts as a sophisticated traffic controller, inspecting all the data coming in and out of your network and blocking anything that doesn't meet the rules you've set. A properly configured firewall is non-negotiable for fending off external threats.
Imagine you run a small retail shop. You could set up a firewall rule that says your point-of-sale (POS) terminals can only talk to the payment processor's servers—and nothing else. No web browsing, no connecting to other computers on the network. This simple rule drastically contains the damage if one of those critical machines ever gets compromised.
The gold standard here is a 'default deny' policy. This means you block everything by default and only create specific rules for traffic you explicitly want to allow. It ensures only essential communications can happen, closing off countless potential avenues for an attack.
The need for these controls is more urgent than ever. The UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) keeps highlighting the rise in cyber incidents that prey on Wi-Fi weaknesses. You can find more details in the latest cyber threat trends from the NCSC Annual Review 2025.
Of course, securing your network perimeter is only half the battle. You also need to think about the various secure remote access methods for connected devices to ensure your systems are protected from every angle.
Use Time-of-Day Restrictions
Here’s another incredibly effective, and often overlooked, policy: limit when your network is available. Most business-grade routers let you set time-of-day restrictions, which can automatically disable certain networks outside of your operating hours.
A perfect use case is your guest Wi-Fi. You can schedule it to switch off automatically at 6 PM and turn back on at 8 AM. Why leave a potential gateway into your network wide open and unmonitored all night? This simple bit of scheduling is an effortless way to tighten your security during the times your business is most vulnerable.
Your Top Questions on Business Wi-Fi Security, Answered
Even with the best plan, you're bound to have questions when you start locking down your business Wi-Fi. Let's tackle some of the most common ones I hear from clients. Getting these right will help you focus your energy where it truly counts.
How Often Should We Change Our Wi-Fi Password?
In a business setting, you can't just set it and forget it. I always advise clients to change their main Wi-Fi password at least quarterly. For the router's administrator password, aim for a refresh every six months.
The non-negotiable rule? If an employee who knows these passwords leaves the company, change them the same day. This isn't something to put off until tomorrow. A good password manager makes this whole process much easier, helping you create and track seriously strong passwords without the headache.
Is Hiding the Network Name (SSID) Worth It?
Honestly, not really. Hiding your SSID is what we call "security through obscurity," and it's a very flimsy defence. It might stop a casual snooper, but anyone with a bit of know-how can use common network tools to find your "hidden" network in minutes.
You're far better off spending that time and effort on measures that actually work. Focus on implementing rock-solid WPA3 encryption, using a properly complex passphrase, and ensuring your router’s firmware is always up to date. These are the things that build a real wall around your network; hiding the name is like putting up a flimsy curtain.
If you do only one thing today, make it this: change the default administrator username and password on your router. These factory settings are often public knowledge, and leaving them as-is is like leaving the front door to your entire network wide open.
What’s the Single Most Important Step to Take Right Now?
Locking down your router's admin access is, without a doubt, your number one priority. Once that's sorted, immediately check that your network is using WPA3 encryption (or WPA2-AES at a minimum). Just doing these two things will shield you from the most glaring and dangerous vulnerabilities that businesses typically face.
It's a harsh truth, but most security breaches aren't sophisticated hacks; they start by exploiting simple mistakes. The 2025 Cyber Security Breaches Survey, commissioned by the UK government, revealed that a staggering number of businesses reported some form of cyber attack. Many of these incidents begin with an attacker finding an easy way in through an insecure Wi-Fi network with a weak or default password. You can dig into the details by reading the UK government’s findings on cyber security breaches. Taking these foundational steps seriously is your best and most effective line of defence.
At SES Computers, we live and breathe this stuff. We provide managed IT support and cyber-security services that help businesses across the South of England protect what matters most. If you’d rather have an expert handle your network security, get in touch with us at https://www.sescomputers.com.